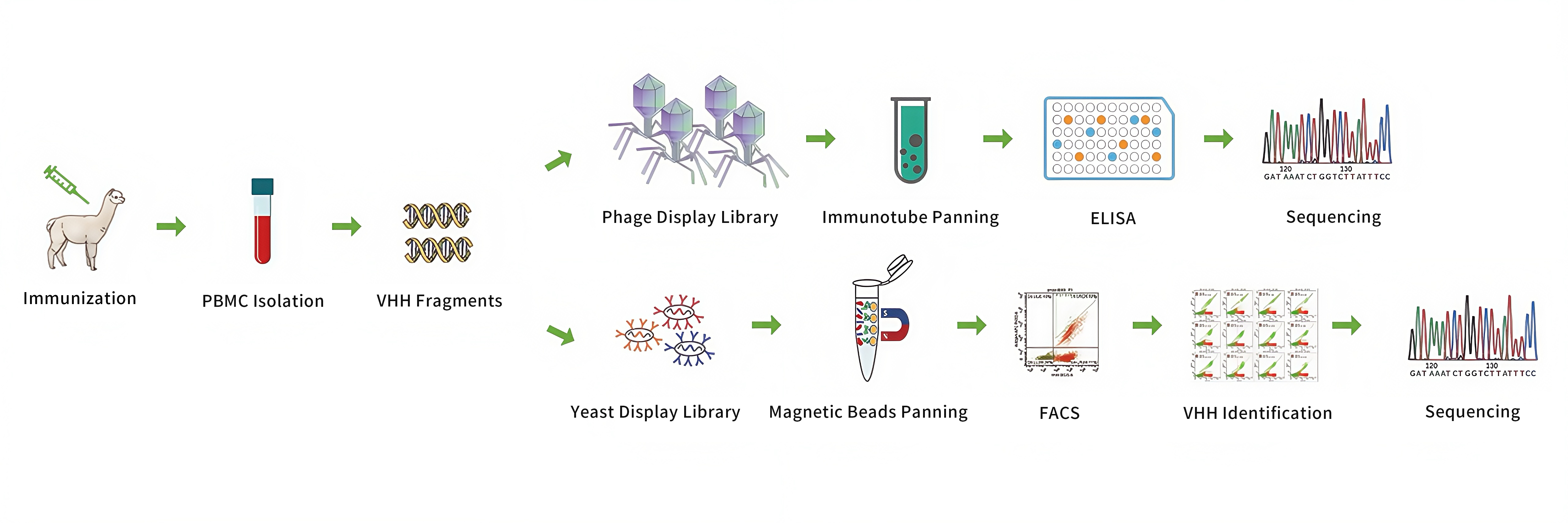
Phage Display Library Construction
Construct diverse VHH DNA sequences in phagemids, transform into TG1 competent cells, culture and induce VHH display on phage surface.
Yeast Display Library Construction
Insert diverse VHH DNA sequences into the display plasmid vector containing the protein scaffold-Aga2 gene, and transform into the competent yeast cells to prepare the yeast display library.
Technical Advantages
Extracted high quality RNA lays a solid foundation for library construction.
Optimized primers can ensure VHH library diversity.
Customized VHH Antibody Discovery Service - Phage Display Method
| Service | Progress | Dliverable | Time |
|---|
| Alpaca Immunization | Antigen emulsification;
Animal immunization;
Blood collection;
PBMC isolantion | Immunization report | ~ 2 month |
Library Construction
| Isolation of total RNA;
cDNA synthesis;
VHH fragment amplification;
Plasmid construction;
Phage library amplification
and purification | Phage library
All the original data
Project report
| ~ 1.5 month |
Phase Display
&
Panning
| Antigen immobilization;
Phase selection by 3 rounds of
panning
| Project report | ~ 2 weeks |
Screening and
Characterization
| Phase clone screening by ELISA;
VHH DNA sequencing
| VHH sequences
Project report | ~ 1 month
|
Customized VHH Antibody Discovery Service - Yeast Surface Display Method
| Service | Progress | Dliverable | Time |
|---|
| Alpaca Immunization | Antigen emulsification;
Animal immunization;
Blood collection;
PBMC isolantion | Immunization report | ~ 2 month |
Library Construction
| Isolation of total RNA;
cDNA synthesis;
VHH fragment amplification;
Plasmid construction
| Phage library
All the original data
Project report
| ~ 2 weeks |
Yeast Display Library
Construction | Yeast transformation and library
generation | Yeast display library;
Project report
| ~ 2 weeks |
Panning by MACS and
FACS | Magnetic selection followed by
FACS for cell sorting
| Project report | ~ 1 month |
Screening and Analysis
of Selected Clones | Individual yeast clone analysis;
Sequencing
| VHH sequences;
Project report | ~ 1 month
|


